Abstract
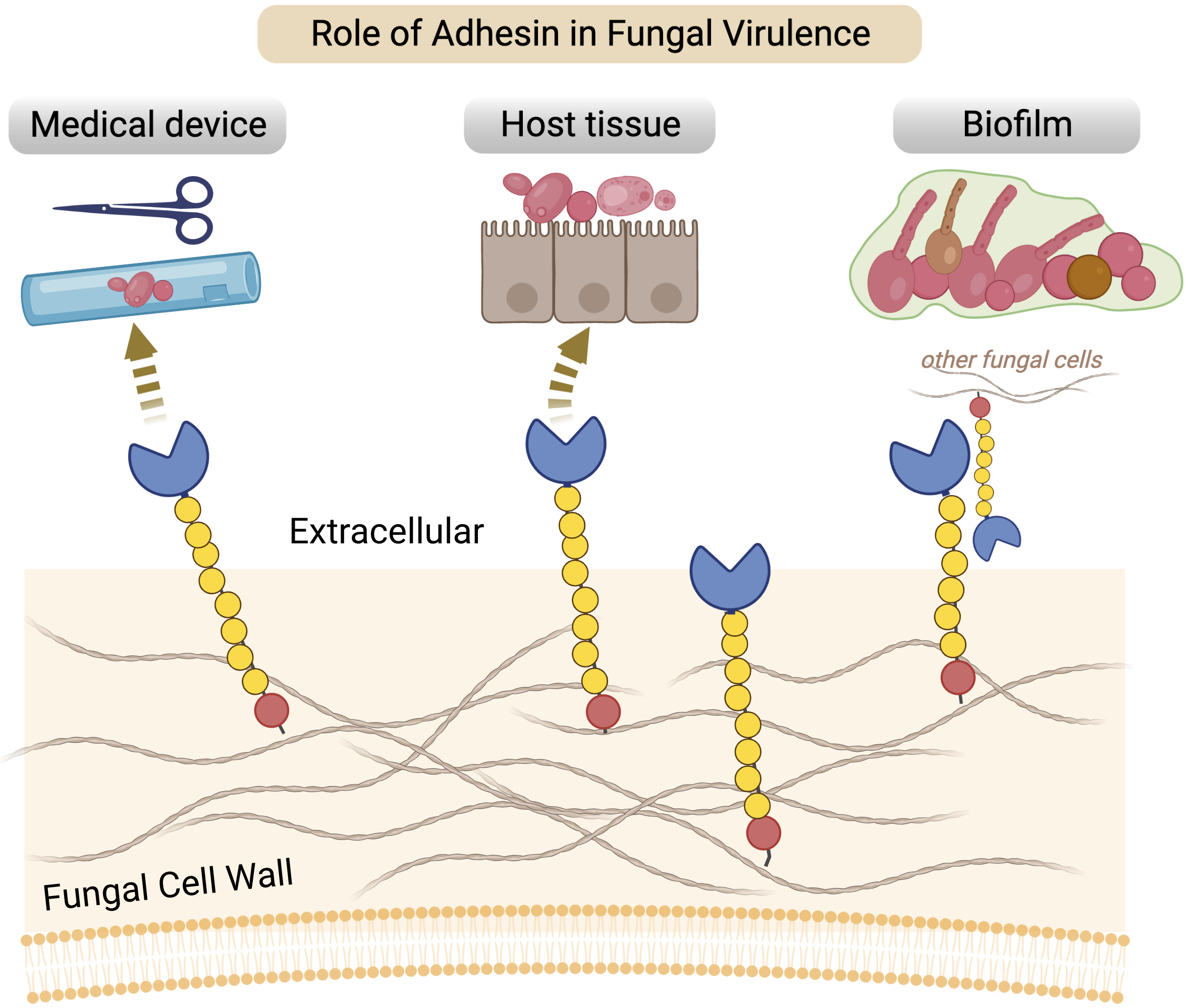
Opportunistic yeast pathogens arose multiple times in the Saccharomycetes class, including the recently emerged, multidrug-resistant (MDR) Candida auris. We show that homologs of a known yeast adhesin family in Candida albicans, the Hyr/Iff-like (Hil) family, are enriched in distinct clades of Candida species as a result of multiple, independent expansions. Following gene duplication, the tandem repeat–rich region in these proteins diverged extremely rapidly and generated large variations in length and β-aggregation potential, both of which are known to directly affect adhesion. The conserved N-terminal effector domain was predicted to adopt a β-helical fold followed by an α-crystallin domain, making it structurally similar to a group of unrelated bacterial adhesins. Evolutionary analyses of the effector domain in C. auris revealed relaxed selective constraint combined with signatures of positive selection, suggesting functional diversification after gene duplication. Lastly, we found the Hil family genes to be enriched at chromosomal ends, which likely contributed to their expansion via ectopic recombination and break-induced replication. Combined, these results suggest that the expansion and diversification of adhesin families generate variation in adhesion and virulence within and between species and are a key step toward the emergence of fungal pathogens.